Do you want to root your Android smartphone so you can unleash the true power of your device? Thankfully, the process isn’t as difficult as you may think. But what happens when things change and you find you just don’t use root applications as much as you thought you would? If you’re in a situation like this, unrooting your phone actually makes sense. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to unroot any Android device.
Table of Contents:
What is Unrooting?
Unrooting an Android device is the process of retracting all the elevated permissions and access as a root user. Since rooting usually involves modifying the boot partition, you might just want to unroot to take an over-the-air update because it would otherwise fail on a tampered system. Or perhaps you’re trying to sell your device, so you need to restore it to factory settings.
Whatever your reasons are, removing root access isn’t that difficult – as long as you follow the correct procedure.
How to unroot
Like rooting, there are a few different methods of unrooting your phone, and which one you choose depends on the maker of the target device, the version of Android installed on the device, and of course, the method of rooting.
Unroot by uninstalling Magisk
Since there aren’t many alternatives to Magisk when it comes to rooting, your only real option for unrooting is to remove any traces of Magisk from your device. Thankfully, you have two methods you can pick from.
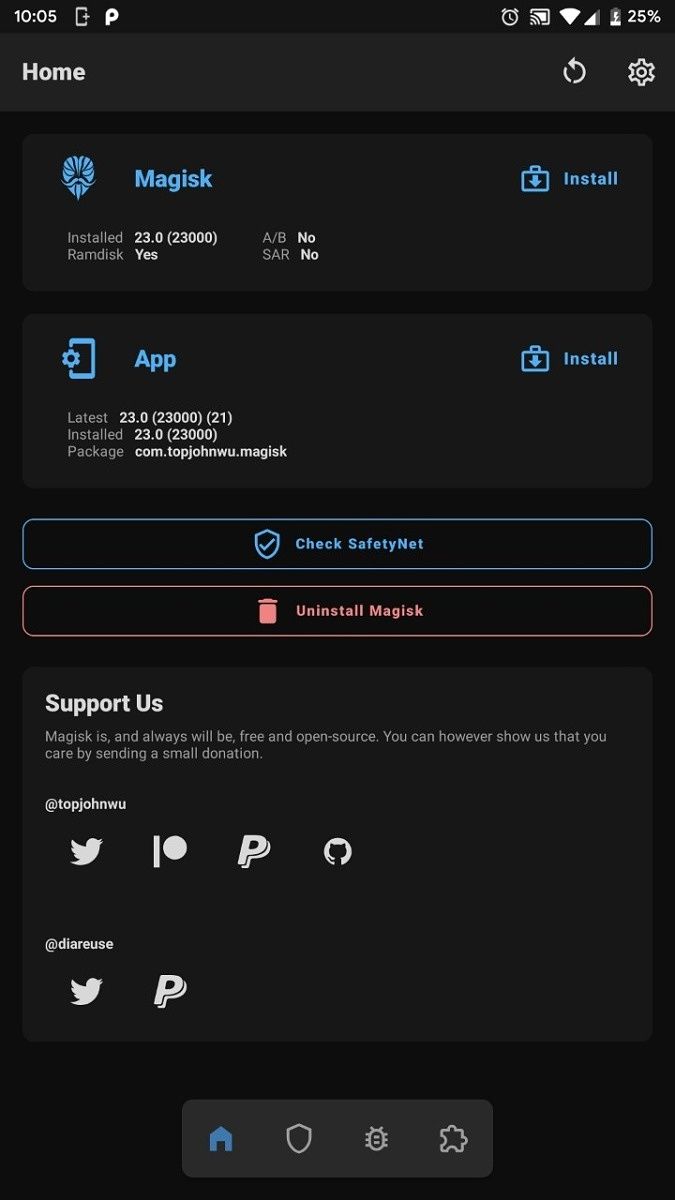
1. Uninstall Magisk from the app
To fully unroot a device originally rooted using Magisk, the most straightforward way is to opt for the built-in “Uninstall” option available on the application itself. After tapping the button, you’ll be greeted with the option to restore the stock partition images and completely uninstall Magisk. To remove Magisk and all modules, tap on “COMPLETE UNINSTALL”.
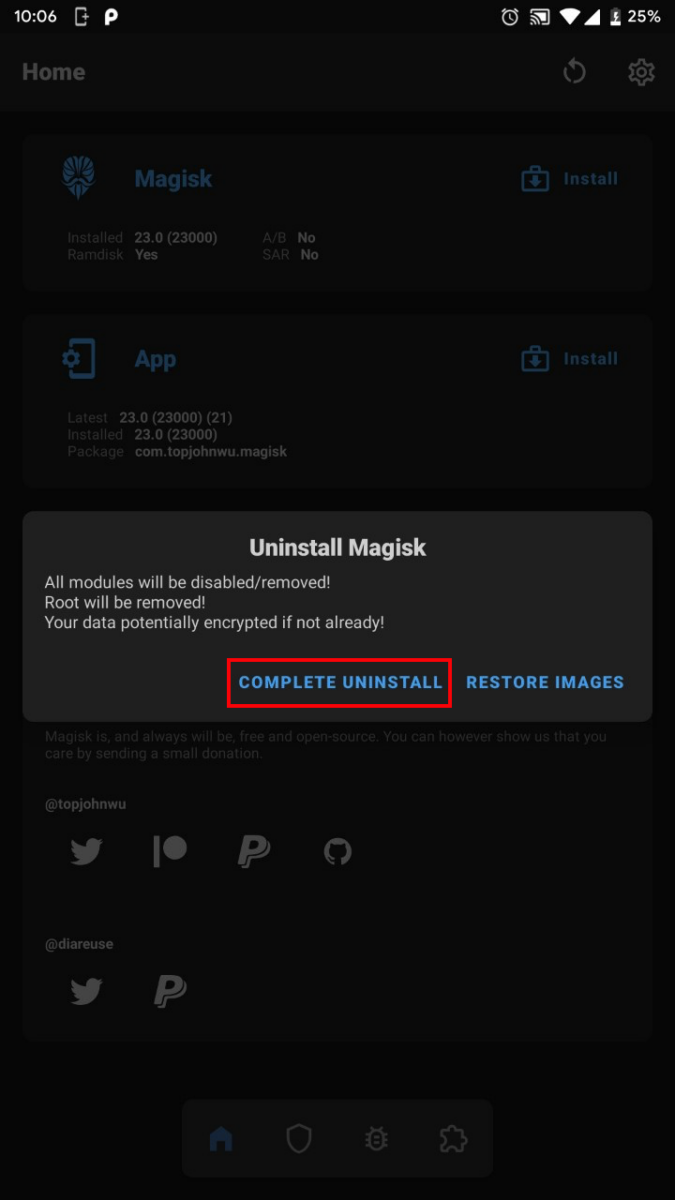
The Magisk app will run the necessary scripts to remove Magisk from your phone and restore your device’s original boot image. As soon as the process ends, the phone will automatically reboot and you’re finished.

2. Uninstall Magisk from TWRP
In case you can’t boot to Android, but have access to a custom recovery like TWRP, you can still uninstall Magisk. To do so, rename the Magisk APK to uninstall.zip, boot to recovery mode, and flash it like any other ordinary flashable zip.

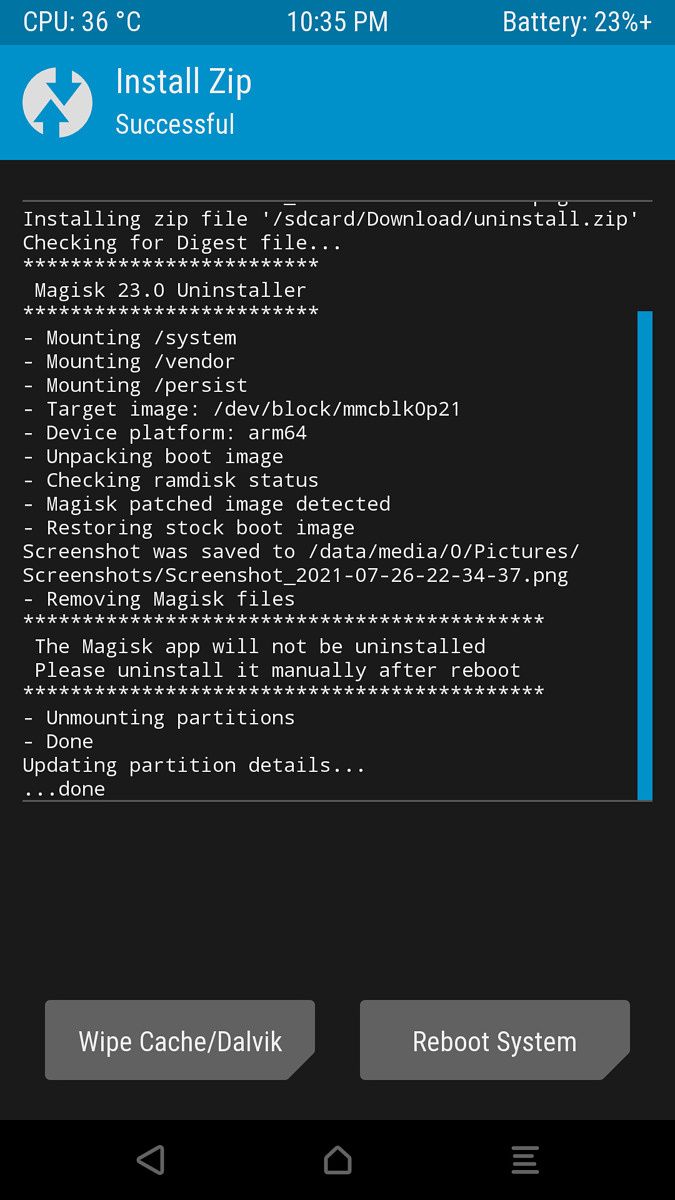
Unroot by flashing the original boot image
Magisk always creates a backup of the stock boot image before patching it. As a result, you can use the Magisk app to restore the backup as shown below. You may need to manually reboot the phone in order for the changes to take effect.

In case you have access to the factory firmware of the exact build installed on your phone prior to rooting, you can also extract the stock boot image and flash it manually to regain the unrooted status. On most devices, you may end up with a file named boot.img which can be flashed using the regular Fastboot utility. However, OEMs like Samsung need special utilities to flash the factory firmware — the details of which are out of the scope of this article.
Unroot by installing an OTA update
Another method to unroot is to install an official OTA update. Google, OnePlus, Xiaomi, and many other Android OEMs offer official download repositories that contain full (i.e. non-incremental) OTA ZIP packages. This is also true for most custom ROMs such as LineageOS. As the full update package can always rewrite the underlying firmware — no matter how far modified it is — end users can utilize this method to restore the stock partition images and get unrooted.
You just have to pick the appropriate OTA ZIP file for your device and install it through the built-in update installer of the OS or using the recovery mode. This is probably the best way to restore your phone if you don’t like mucking around in the Magisk app.
Unroot by installing the stock firmware
While the aforementioned methods of unrooting should theoretically work just fine on devices that have been rooted using the systemless method, it’s still good to know what to do in a situation where restoring the stock boot image may not be able to fully unroot the device. Perhaps you caught up with a bootloop, or you messed up your Wi-Fi connectivity by restoring a wrong boot image?
The good news is reinstalling the stock firmware should do the trick. You’ll need to download the factory image for your device. For Pixel devices, this is provided by Google. Other device images should be provided by their manufacturer. Then use the OEM-described method to install the device software and start from scratch. Keep in mind you will lose your personal data if you follow this route without taking an off-site backup beforehand.
Verification
At this point, you can double-check the root status of the device by using the Magisk app. If its status comes back as not installed, then you’re done!

You can also use an app named Root Checker to do the job. Once installed, open the app and check the status section under the “VERIFY ROOT” tab. You should see something like the following if you’re unrooted.

Root Checker (Free+, Google Play) →
And that’s it! Unrooting your phone is an easier task than rooting, and we hope our guide made the process even easier for you to understand and follow.
The post How to Unroot your Android phone appeared first on xda-developers.
from xda-developers https://ift.tt/2Vkfw0g
via
IFTTT